Fibonacci retracements are a widely used and reliable tool for predicting potential support and resistance levels. The Fibonacci tool is based on the principle that markets often retrace a portion of a previous move before continuing on the dominant trend.
Traders use the Fibonacci tool on platforms like MT4 and MT5 to connect the lows and highs of recent trends, swings, or ranges, displaying likely levels where the price might reverse or pause, based on the Fibonacci Sequence (also known as the Golden Ratio).
In this article, we’ll delve into how Fibonacci retracements work, how to use them effectively, and why they’re so useful in Forex trading.
What Are Fibonacci Retracements?
Fibonacci retracements are a technical analysis tool used to identify potential levels of support and resistance in the market. These levels are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a mathematical sequence where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones (e.g., 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21…). The key retracement levels most traders use are:
- 23.6%
- 38.2%
- 50% (though not part of the Fibonacci sequence, this level is widely used due to its historical relevance)
- 61.8%
- 78.6%
These levels help traders identify where the price is likely to reverse or pause within an existing trend. Fibonacci retracements are effective because they reflect natural patterns in market behaviour, and these levels frequently coincide with historical support or resistance zones.
How Fibonacci Retracements Work
To apply Fibonacci retracements, traders use the Fibonacci tool to connect the highest and lowest points of a trend or swing. The retracement levels are then plotted on the chart, providing a roadmap for potential support and resistance areas.
Example: USDCAD Down Move
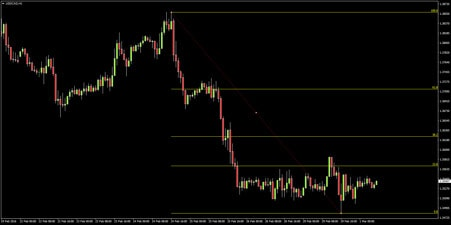
Let’s look at a recent down move in USDCAD. By applying the Fibonacci tool from the recent peak (the high) to the range low (the bottom), the Fibonacci tool reveals several potential resistance levels:
- 23.6%
- 38.2%
- 50%
- 61.8%
- 78.6%
As you can see, the price encountered resistance near the 23.6% level multiple times, failing to break above it.
We’re also seeing a false break above the 23.6% level in February, but the price ultimately couldn’t hold and continued its downward trajectory. Once the price breaks below a key Fibonacci level like 23.6%, traders often use the next Fibonacci levels (38.2%, 50%, etc.) to gauge further resistance points.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracements in Forex
Fibonacci retracements can be used in both downtrends and uptrends to identify potential price levels for reversals or continuation:
1. In a Downtrend
- Identify the High and Low: When the price is in a downtrend, use the Fibonacci tool to connect the recent high to the low.
- Watch for Resistance: The retracement levels (23.6%, 38.2%, 61.8%, etc.) will show areas where the price may encounter resistance as it retraces upwards.
- Enter a Short Trade: When the price hits one of these levels and shows signs of resistance (e.g., candlestick patterns, MACD divergence), traders may look to enter a short position.
2. In an Uptrend
- Identify the Low and High: In an uptrend, apply the Fibonacci tool from the low to the high.
- Watch for Support: The Fibonacci retracement levels will now show potential support areas where the price may pull back before continuing higher.
- Enter a Long Trade: If the price retraces to one of these levels (e.g., 50% or 61.8%) and shows buying interest, traders might enter a long position.
Practical Example: Trading with Fibonacci Retracements
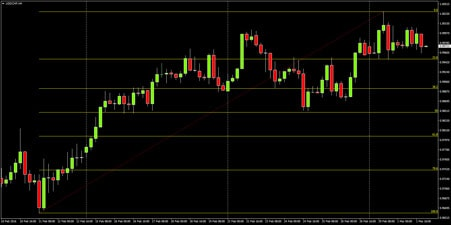
Let’s look at an example using USDCHF. After identifying the current uptrend, a trader uses the Fibonacci tool to connect the low and high of the recent rally. The key Fibonacci levels now serve as potential support areas for the price to pull back to.
Two Options for Entering a Trade:
- Wait for a Correction to the 50% Level: A more cautious approach involves waiting for the price to correct to around the 50% level and show signs of support before entering a long position. This offers a safer, more conservative entry.
- Place a Buy Limit Order: If the trader is more confident in the setup, they may choose to place a buy limit order just above the 50% level to enter the market immediately when the price approaches this support level.
Stop-Loss Placement:
Once the trader enters the market, they need to determine where to place their stop-loss order. There are a few options:
- Tight Stop: Place the stop just below the 50% level.
- Reasonable Stop: Place the stop below the 61.8% level, which provides a bit more room for price fluctuation.
- Loose Stop: A more extended stop below the 78.6% level for traders willing to take on more risk.
- Invalidation Stop: If the price moves below the 100% level, the trader’s bullish thesis is invalidated, and the position should be exited.
When Fibonacci Retracements Fail
Like all tools, Fibonacci retracements are not infallible. Sometimes, the price may breach key retracement levels, or the retracement may not even reach the expected levels. A break beyond the 78.6% level often signals a major trend reversal or a range-bound market.
This is why risk management is key. Always use stop-loss orders and position sizing to manage your risk, and avoid placing trades blindly based on Fibonacci alone. Combine Fibonacci levels with other tools like trend lines, candlestick patterns, and momentum indicators for more robust trading strategies.k
To effectively use Fibonacci retracements in your trading, remember to always wait for confirmation (e.g., price action, candlestick patterns) before entering a trade and ensure proper risk management through stop-loss orders. When used alongside other technical analysis tools, Fibonacci retracements can become a powerful addition to your trading strategy.



